Aloe Vera & TEER
Aloe Vera and the effect on biological membrane permeation and Intestinal drug absorption enhancement.
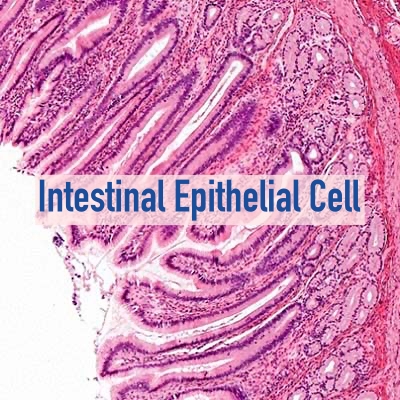
The polysaccharides in the Aloe Vera are responsible to contribute to a large extent to the effect on the TEER of the excised rat intestinal tissueIf the size of the openings of the tight junctions increases in the presence of a paracellular permeability enhancer. The TEER of the intestinal epithelium will be reduced because of the increasing flow of ions through the opened tight junctions and intercellular spaces This reduction in TEER of the excised rat intestinal.
Tissue by the Aloe Vera indicates their ability to open the tight junctions between epithelial cells, which indicate the potential of these materials to enhance drug transport across intestinal tissues. TEER is a measure of tight junction integrity between adjacent intestinal epithelial cells. If the size of the openings of the tight junctions increases in the presence of a paracellular permeability enhancer, the TEER of the intestinal epithelium will be reduced because of the increasing flow of ions through the opened tight junctions and intercellular spaces.
Tight junctions between epithelial cells are dynamic structures that can be modulated by certain chemicals in such a way to enlarge the pores or fenestrae and thereby allow paracellular passage of hydrophilic macromolecules. This approach to drug absorption enhancement has the additional Advantage of avoiding enzymatic degradation of susceptible molecules. Aloe Vera Compounds selectively open the intestinal epithelial tight junctions, referred to as paracellular permeability enhancers, have shown potential as novel excipients in advanced drug delivery systems.
It is well known that polysaccharides of natural origin such as Aloe Vera are capable of enhancing the intestinal absorption of co-administered drugs by means of a transient opening of the tight junctions between adjacent epithelial cells to allow for paracellular transport across the intestinal epithelium.
Aloe Vera Gel Extract could decrease the transepithelial electrical resistance of intestinal epithelial cell monolayers (Caco-2), thereby indicating opening of the tight junctions between adjacent epithelial cells. Aloe Vera Gel is also able to significantly increase the transport of the macromolecular peptide drug, insulin, across the Caco-2 cell monolayers.
Many potential therapeutic agents face the disadvantage of low bioavailability after oral administration due to poor membrane permeability. Drug absorption enhancers are compounds capable of reversibly removing the resistance of the outer layers in the body with minimum tissue damage, thus allowing the drug to enter the blood circulation in sufficient quantities. Although many compounds have been investigated for their drug absorption enhancing properties, some have been associated with cytotoxic effects and others were not efficient enough to ensure that therapeutic levels of poorly absorbable drugs are achieved. Only limited information is currently available on the drug absorption enhancement activities of A. vera gel, but if it proves to be a safe and effective absorption enhancer in vivo, it could be used in novel dosage forms for the oral delivery of poorly absorbable drugs that are administered by means of injections.
“disclaimer” that FDA has not evaluated the claim. The disclaimer must also state that the dietary supplement product is not intended to “diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease,”because only a drug can legally make such a claim.

