Acemannan
Unleash Nature’s Potential with Acemannan in Bulk from AMB Wellness
All you need to know about
Acemannan & Aloe Vera
How does Acemannan work in ACETYPOL?
In today’s evolving marketplace, the influence of consumer perception is highly visible in the growing realm of natural products. As a result, manufacturers must be ready to channel consumer interest into innovative offerings. The shifting landscape has catalyzed the creation of fresh natural applications, with Acemannan (Aloe Vera) being the superior ingredient for any natural derivative.
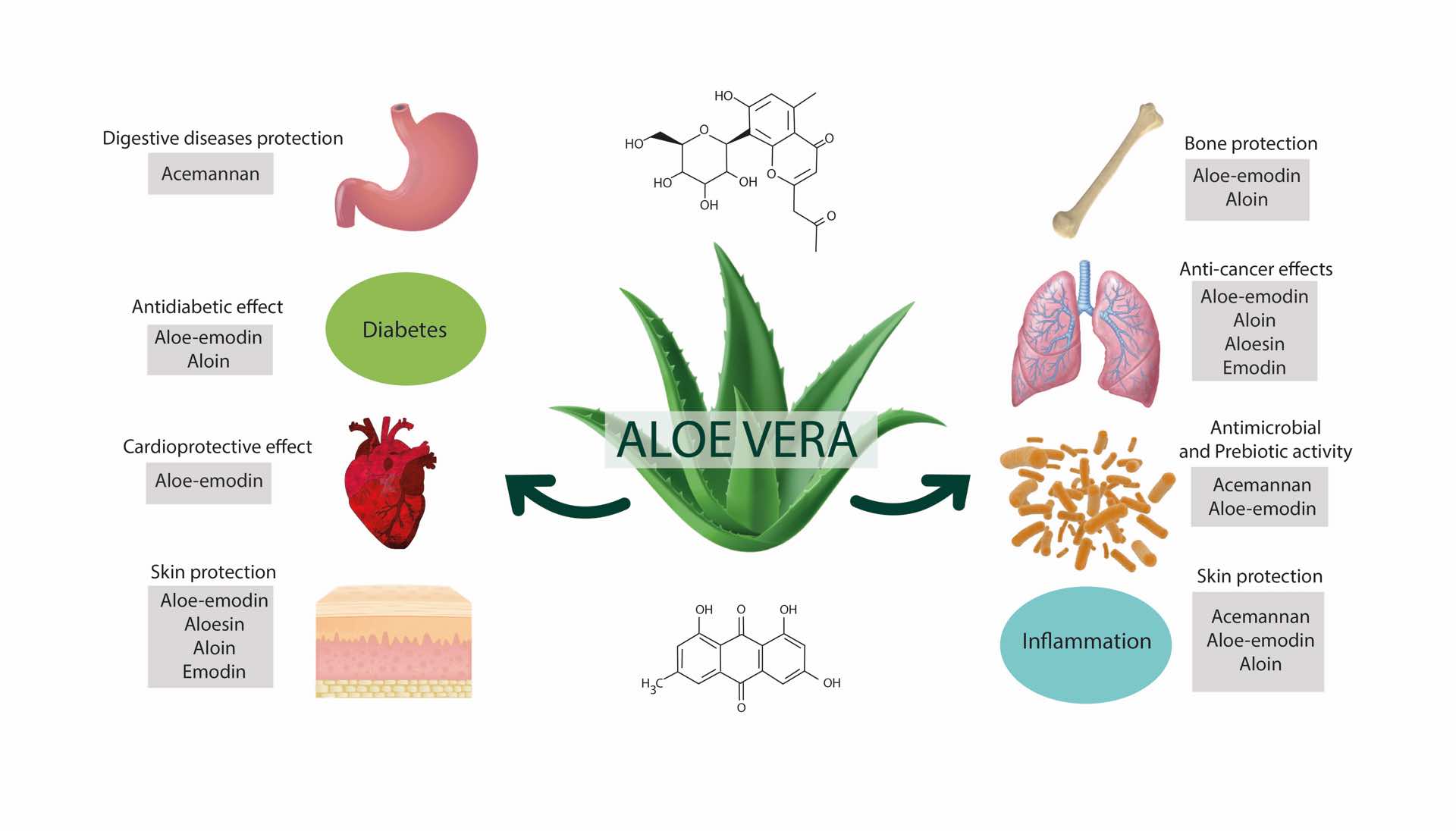
Aloe Vera carries a longstanding acceptance as a plant possessing powerful healing properties. Over recent years, an array of scientifically validated books and articles on Aloe Vera has emerged. Institutions like the International Aloe Science Council (IASC) and acclaimed healthcare entities, supported by their publications and physician case histories, have affirmed the ‘Aloe phenomenon’.
The significance of compounds present in Aloe is underscored by their inclusion in every notable pharmacopeia. Varying with the processing method of the leaves, mucilage and sugars form the primary constituents of desiccated gel. Although there have been differing reports, the mucilage is primarily composed of a polysaccharide called mannan or glucomannan.
The majority of the gel is polysaccharide-based mucilage with trace quantities of other compounds. It’s noteworthy that the observed activities indicate a possible synergistic interaction between the polysaccharide base and other ingredients.
The polysaccharides found in Aloe have a distinctive capacity to adhere to extracellular membranes, thus enhancing their inherent permeability. Consequently, Aloe boosts cellular nutrient and oxygen delivery while facilitating the elimination of metabolic waste.
Acemannan Enhancing Properties
Work the wonders of Aloe Vera with Aloe Lignins, the driving force behind the gel’s ability to permeate deeply into your skin’s layers. This property is crucial when administering a healing solution for skin conditions, amplified by the presence of salicylic acid and other anti-prostaglandin compounds. These components assume a formidable role in local anti-inflammatory activity, likely due to their inhibitory influence on the arachidonic acid cycle via cyclooxygenase.
Lignin, a cellulose-based substance, may lack outright medicinal attributes, but it offers your skin a unique advantage. When Aloe Vera is topically applied, it’s the Lignin that facilitates penetration through human skin all the way to the dermis layer, where the genesis of new skin cells occurs.
In the heart of Aloe Vera lies Lignin, the primary structural material of cellulose that enables the gel’s deep penetration properties. In fact, it’s proven that Aloe Vera can penetrate unto seven skin layers deep. This penetrative prowess proves especially beneficial for skin issues such as eczema and psoriasis, particularly hard for other products to breach.
This cellulose substance found in the gel, despite holding no explicit medicinal advantages, does boast a unique ability – it enables deep skin penetration. Combine this with the anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties of Aloe’s salicylic acid components, and the result is nothing short of miraculous pain relief.
The Phenolic compounds present an additional benefit for your overall wellness. They stimulate bowel movement and display anti-biotic properties, assisting with gastric motility and softening stools. Lignins constitute a sizable portion of cellulose, an insoluble fibrous substance that forms plant cell walls and provides Aloe with its penetrative traits.
This is how Aloe Vera, armed with Lignins, can permeate your skin as deep as three layers. The potential for Lignins to infiltrate even tough skin areas offers significant relief for skin conditions like eczema and psoriasis, underscoring the comprehensive nature of Aloe’s treatment capabilities. Let AMB Wellness’s Aloe-based products help unlock the full potential of these properties for you today.
Aloe Acetypol is ideal for enhancing skin penetration.
Experience the magic of Aloe Vera with Aloe Lignins, the powerhouse behind the gel’s deep skin-penetrating ability. When administering a healing solution for skin conditions, this property is amplified by the presence of salicylic acid and other anti-prostaglandin compounds. These components play a supreme role in local anti-inflammatory activity, likely due to their inhibitory effect on the arachidonic acid cycle via cyclooxygenase.
Lignin, a cellulose-based substance, may not possess explicit medicinal properties, but it provides your skin with a unique benefit. When Aloe Vera is topically applied, it’s the Lignin that allows it to penetrate human skin all the way to the dermis layer, where new skin cells emerge.
At the center of Aloe Vera lies Lignin, the primary structural material of cellulose that empowers the gel’s deep permeability properties. It’s been proven that Aloe Vera can penetrate up to seven skin layers deep. This penetrative ability is particularly useful for skin conditions like eczema and psoriasis, which are typically challenging for other products to reach.
The cellulose compound in the gel may not possess explicit medicinal advantages but does boast a unique trait – it enables deep skin penetration. This, combined with the anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties of Aloe’s salicylic acid elements, results in miraculous pain relief.
Phenolic compounds offer additional wellness benefits. They stimulate bowel movements, have antibiotic properties, aid gastric motility, and soften stools. Lignins make up a considerable portion of cellulose, an insoluble fibrous material that forms plant cell walls, giving Aloe its penetrative traits.
This is how Aloe Vera, equipped with Lignins, can penetrate your skin up to three layers deep. The ability of Lignins to infiltrate even tough skin areas provides significant relief for conditions like eczema and psoriasis, underscoring the comprehensive nature of Aloe’s treatment capabilities. Experience the full potential of these properties with AMB Wellness’s Aloe-based products today.

Understanding the emerging trends in the wellness industry, AMB’s R&D department has adoptive policies to innovate and produce products tailored to the distinct formulations required by our clients. One of our most potent offerings includes our Aloe Vera extracts, noted for their high polysaccharide and notably superior Acemannan content. These extracts can be seamlessly integrated into formulations designed for skin hydration, anti-inflammatory solutions, lightening products, and hair care remedies.
With a rising demand for specialized products, AMB Wellness presents ACETYPOL, our latest innovation aimed at providing moisturizing skincare solutions. This unique product is synthesized through an exclusive AMB Wellness proprietary technique involving the micro filtration of Aloe Vera Gel, retaining polysaccharides up to 50,000 Da. The finished product boasts a polysaccharide composition of 30-35%, as confirmed by HPLC/GPC, with Acemmanan constituting 60% of this quantity.
Advancements in understanding our body’s functions and chemistry have underscored the need for natural ingredients like Aloe Vera. Aloe Polysaccharides, in particular, play a crucial role in promoting healthier skin. To retain the bioactive components of natural extracts, AMB Wellness ensures that the qualities of Aloe Vera are retained in the final products.
Become part of the AMB Wellness story today and experience the unparalleled quality and value of our offerings. With ACETYPOL, we invite you to delve into the healing power of nature, specifically harnessed from Aloe Vera. Join us in educating audiences about this natural treasure and realize your wellness objectives with our curated products.
Choose ACETYPOL, choose excellence. Our superior quality Aloe Vera and Acemannan products are ideal partners for your R&D projects, especially those focused on natural health and skincare regimes. They offer a robust base for your research, ushering in innovative solutions in the natural health and skincare landscape.
We applaud our esteemed clients for their kind words as they succinctly encapsulate the value and impact of ACETYPOL’s Aloe Vera and Acemannan products. Let their words inspire you to invest in high-quality, reliable, and effective R&D tools for your unique projects.
Elevate your research and development with the transformative potential of ACETYPOL’s superior Aloe Vera and Acemannan products today. Begin your journey with us and discover the AMB Wellness difference.

ACETYPOL™
Ideal for creating luxury cosmetics, healthcare products, and nutraceuticals, ACETYPOL™, powered by its high efficacy and superior quality, stands out for R&D departments in search of excellence. It aligns perfectly with the innovative expectations of the nutraceutical and functional food sectors, aiming to pioneer advanced delivery systems. High-end product formulations rely on specially tailored components or excipients, a role effectively executed by ACETYPOL™.
ACETYPOL™ distinct properties are a game-changer for any product application, boosting market performance, adding value, and ensuring user benefits. Our Aloe Vera products are at the cutting edge of nutraceutical research and the booming natural healthcare sector.
Significant ACETYPOL™ attributes for R&D innovations include:
• Concentrated quantities of acetylated polysaccharides, highly valued in nutraceutical research.
• Optimal distribution of molecular weight, vital for reliable and effective natural health products.
• Acts as an excellent ingredient enhancer in the creation of high-end natural skincare and health solutions.
ACETYPOL™ is your reliable partner for the future of natural wellness and beauty, consistently raising the bar in R&D-focused natural products.
What is Acemannan?
Acemannan, often identified with Aloe beta-glucomannans, acetylated polymannans, and mucopolysaccharides, is a long-chain polysaccharide that plays a key role in cellular health. Its primary function includes integrating with all cell membranes, increasing their fluidity, and enhancing permeability. As a result, Acemannan facilitates a toxin detoxification process, allowing harmful substances to exit the cell with ease while letting crucial nutrients in.
Also known as Poly Acetyl Mannose or Poly Acetylated Mannans, Acemannan brings the promise of improved cellular metabolism. It is a critical ingredient in Aloe Vera, contributing to the plant’s extensive health benefits and driving the base for research and development in the natural health and skincare industry.
Renowned for its optimal molecular weight distribution, Acemannan in Aloe Vera plays a pivotal role as a potent immuno-modulator. It is comprised of a highly dispersed ß1,4-linked acetylated polymannan, weighing between 1 to 2 million Daltons. Noticeably found within the inner leaf parenchyma of Aloe Vera leaves, Acemannan highlights a broad molecular weight spectrum, reaching from the low thousands to the low millions.
The natural health benefits of Acemannan are numerous. It is a powerful anti-inflammatory agent assisting in the body’s defense mechanism. Moreover, Acemannan protects the body from damage due to chemical toxins while simultaneously stimulating the immune system. Acknowledged for its role in boosting metabolism and enhancing energy levels, Acemannan is a natural bio-stimulant and a core component of high-quality Aloe Vera and Acemannan R&D products like ACETYPOL.

Acemannan, a key component of Aloe Vera, reinforces the body’s natural immune response against harmful pathogens such as parasites, bacteria, fungi, and viruses. This critical ingredient has demonstrated multiple therapeutic advantages, particularly in addressing immunodeficiency. Glucomannan and Acemannan, both essential contributors to the Aloe Vera benefits, assist in heightened wound recovery and activate macrophages for efficient immune response.
Used widely in natural health R&D, Aloe Vera exhibit superior anti-viral and anti-bacterial properties. It strengthens overall immune functioning, offering a robust defense against intravascular bacteria. The remarkable anti-inflammatory component of Aloe Vera highlights its unique polysaccharide composition.
The body’s native “complement system” – an integral network of proteins in defensive mechanism – can be activated to counter bacterial threats. Triggered by the polysaccharides within Aloe Vera, these proteins initiate a sequence known as the “cascade phenomenon”, forming a unique configuration that intertwines with bacterial surface membranes.
This knowledge of Acemannan and its notable contributions to health and skincare have led to its popularity within R&D departments and academic research related to the skincare industry, natural health sector, and nutraceutical research.
Technical Details
- Immunomodulatory Acemannan < 400 KDa
- Polymeric Acetylated Mannans Content in the soluble fraction (NLT 30%)
- A wide spectrum of Molecular Weight Polysaccharides
- Polysaccharide Content – On Average 20%
- Aloin Content NMT 10 PPM
- Fiber Content (Insoluble Carbohydrates) NLT 30%
- Proprietary Processing technology

Properties of Acemannan
Characterized by wide utility and profound healing properties, Aloe barbadensis Miller, often referred to as the “real aloe,” is a common component in skincare and health products. Conversely, Aloe arborescens Miller, a popular traditional remedy in Japan, is used to treat a broad spectrum of conditions, from digestive problems to athlete’s foot. As a perennial succulent, Aloe Vera features robust, fleshy leaves arranged in a rosette pattern around the stem. Fully matured plants bear leaves exceeding 25 inches in length, adorned with sharp, saw-like spikes along their borders. In the realm of natural health R&D, these plants play a vital role due to the presence of a powerful polysaccharide — Acemannan.
Aloe vera contains two major liquid sources, a yellow latex (exudate) and a clear gel (mucilage). The dried exudate of Aloe barbadensis Miller leaves is referred to as Aloe Vera. The mucilaginous jelly from the parenchymal cells of the plant is referred to as Aloe vera gel. There are generally no anthraquinones to decompose and cause discoloration of the gel unless an improper processing technique contaminates it.
Freshly excised from the plant, Aloe vera gel has been used for centuries by those living where the plant naturally grows as a health and beauty aid.
Aloe vera gel is about 98.5% water by weight. More than 60% of the total solid is made up of polysaccharides of carbohydrate origin. Organic acids and inorganic compounds, especially calcium oxalate, account for the remainder of the solid residue. Whole leaves, exudates, and fresh gels of Aloe plants have been used for several human afflictions. Evidence of their use as a medicinal remedy can be traced to the Egyptians of 400 BC. Aloe vera was also used to embalm the dead and protect the embalmers from the death-causing agent. Other early civilizations used Aloe vera for skincare, to relieve insect stings and bites, to treat scratches and ulcerated skin, to promote wound healing, to prevent hair loss, and as a purgative. Aloe vera was used in the traditional medicine of many cultures as an anthelmintic, cathartic and stomachic and was used for leprosy, burns and allergic conditions. Depending on how the leaves are processed, mucilage and sugars are the major components of the dehydrated gel. The sugars found are galactose, glucose, mannose, rhamnose, xylose, and uronic acids. Although reports conflict, the mucilage is mainly composed of mannan or glucomannan.

For a long time, the controversy over the active substance(s) identity in Aloe vera was not settled. Therefore, it is essential to clearly distinguish between the components present in the gel and those found in the exudates. A majority of the gel is a mucilage of mainly polysaccharide nature with minor amounts of various other compounds. It has been observed that in some of the activities, there may be some synergistic action between the polysaccharide base and other components.
Literature which reports that polysaccharides possess pharmacological and physiological activities continues to flood the pages of well-respected scientific journals. It is, therefore, logical that the mucilaginous gel of the Aloe vera plant, which is essentially a polysaccharide, holds the secret to Aloe vera’s medicinal properties. The controversy over whether the polysaccharide is a glucomannan, mannan, pectin, or other composition, is resolved by a series of chemical purification steps.
Exploring the Chemical Structure of Acemannan in Aloe Vera Products
Delve into the unique chemical characteristics of Acemannan, an active polysaccharide present in Aloe Vera. Our comprehensive review touches on the solubility profile, structural configuration, and acetylation degree of Acemannan – critical pointers for R&D departments focusing on natural healthcare products. Acemannan, a poorly soluble substance in water and dimethyl sulfoxide, forms a significant part of Aloe Vera’s composition, playing a pivotal role in the plant’s healing capabilities.
Commonly depicted as a fluffy, white, slightly hygroscopic powder, Acemannan stands out in organic chemistry for its insolubility in most organic solvents, a trait marked by its unique linear b(1-4)-D-mannosyl units. The long-chain polymer is laced with randomly interspersed acetyl groups that connect to the polymer through an oxygen atom, shaping the definitive structure of Acemannan.
For R&D teams examining Aloe Vera benefits or working towards Aloe Vera product formulation, understanding Acemannan’s chemical properties becomes vital. This ingredient’s degree of acetylation, estimated at approximately 0.91 acetyl groups per monomer, is determined using the alkaline hydroxamate method. This information is critical for research focused on the development of natural skincare and health remedies.
Looking to integrate Acemannan’s unique chemical properties into your R&D? Dive deeper into the fundamental attributes of Acemannan – a powerful polysaccharide altering the course of natural health product development.
Acemannan is a fluffy, white, amorphous, slightly hygroscopic powder, which is poorly soluble in water and dimethyl sulfoxide and insoluble in most other organic solvents. This powder consists of linear b(1-4)-D-mannosyl units. The polysaccharide is a long chain polymer interspersed randomly with acetyl groups linked to the polymer through an oxygen atom. The generic name for the polymer is acemannan. The degree of acetylation is approximately 0.91 acetyl groups per monomer as determined by the alkaline hydroxamate method.
Unique Benefits of Acemannan in Natural Skincare R&D
The naturally curative properties of Aloe Vera, specifically Acemannan, have long been recognized in the domain of skincare and healthcare. In recent years, the amount of scientific literature on Aloe Vera has surged, further emphasizing its significance in natural skincare and therapeutic applications. Renowned institutions, such as the International Aloe Vera Science Council, have endorsed this ‘Aloe phenomenon’, echoing its role in clinical case studies and scientific publications.
Moreover, Aloe Vera has been spotlighted within the skincare research and development (R&D) sector for treatment of skin conditions induced by radiation. Its efficacy has been demonstrated in several pharmacology studies and dermatology research.
Acemannan: A Breakthrough in Skincare and Immune Health R&D
Acemannan, a critical component of Aloe Vera, has been revealed to stimulate the immune system effectively. Studies have shown that Acemannan propels the production of Interleukin 1 (Ii-1) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2). Thus, it bridges the gap for bioavailability issues in conventional wound-healing applications, and presents a potential solution for cuts, sores, and ulcer treatment.
Owing to the exceptional therapeutic benefits of Acemannan, research in wound recovery techniques is evolving. While there are multiple modes of treatment available for wound care, like gels and dressings, the actual process of wound healing lacks positive modulatory interventions. Chronic wounds, especially in the elderly and diabetic populations, pose a widespread issue that Acemannan, with its immune-stimulating and wound-healing capabilities, aims to address.
Acemannan in Wound Care and Skincare R&D
Contemporary wound care techniques focus primarily on mitigating ischemic tissues, using methods such as occlusive dressings, vascular grafts, or hyperbaric oxygen. However, Aloe Vera and Acemannan are poised to revolutionize the actively researched realm of wound healing solutions, giving rise to improved natural skin care and healthcare products.
The uphill challenge of improving capillary circulation to peripheral tissues, posed by atherosclerosis or venous stasis, can be tackled with Acemannan’s unique wound-healing benefit.
Cytokines, Growth Factors, and Acemannan
Intensive R&D momentum over the past years has highlighted cytokines and growth factors like fibroblast growth factor, platelet-derived growth factor, and transforming growth factor. Although these proteins have shown topical success, their systemic impact is yet to be evidenced. Given their short biological half-life, the potential for systemic wound healing is marginal. Therefore, the quest for safer, systemically applicable wound-healing agents has led to heightened interest in Acemannan. Its key role in wound recovery and tissue regeneration adds tremendous value to the future of natural skincare and healthcare R&D.
“disclaimer” that FDA has not evaluated the claim. The disclaimer must also state that the dietary supplement product is not intended to “diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease,”because only a drug can legally make such a claim.




